模拟Eq. 10.2¶
| cnblogs | AdaBoost对实际数据分类的Julia实现 |
|---|---|
| 作者 | szcf-weiya |
| 时间 | 2018-01-03 |
| 更新 | 2018-02-28, 2018-05-17@xinyu-intel |
本节是对10.1节中式(10.2)的模拟。
问题¶
特征 $X_1,\ldots,X_{10}$ 是标准独立高斯分布,目标$Y$定义如下
考虑 2000 个训练情形,每个类别大概有 1000 个情形,以及 10000 个测试观测值。若分类器选为“stump”(含两个终止结点的分类树)。
Julia实现¶
Julia的具体细节参见官方manual。
首先我们定义模型的结构,我们需要两个参数,弱分类器的个数 n_clf 和存储 n_clf 个弱分类器的 n_clf$\times 4$ 的矩阵。因为对于每个弱分类器——两个终止结点的stump,我们需要三个参数确定,分割变量的编号idx,该分割变量对应的cutpoint值val,以及分类的方向flag(当flag 取 1 时则所有比 cutpoint 大的观测值分到树的右结点,而 flag 取 0 时分到左结点),另外算法中需要确定的 alpha 参数,所以一个 stump 需要四个参数。下面代码默认弱分类器个数为 10。
struct Adaboost
n_clf::Int64
clf::Matrix
end
function Adaboost(;n_clf::Int64 = 10)
clf = zeros(n_clf, 4)
return Adaboost(n_clf, clf)
end
训练模型
function train!(model::Adaboost, X::Matrix, y::Vector)
n_sample, n_feature = size(X)
## initialize weight
w = ones(n_sample) / n_sample
threshold = 0
## indicate the classification direction
## consider observation obs which is larger than cutpoint.val
## if flag = 1, then classify obs as 1
## else if flag = -1, classify obs as -1
flag = 0
feature_index = 0
alpha = 0
for i = 1:model.n_clf
## step 2(a): stump
err_max = 1e10
for feature_ind = 1:n_feature
for threshold_ind = 1:n_sample
flag_ = 1
err = 0
threshold_ = X[threshold_ind, feature_ind]
for sample_ind = 1:n_sample
pred = 1
x = X[sample_ind, feature_ind]
if x < threshold_
pred = -1
end
err += w[sample_ind] * (y[sample_ind] != pred)
end
err = err / sum(w)
if err > 0.5
err = 1 - err
flag_ = -1
end
if err < err_max
err_max = err
threshold = threshold_
flag = flag_
feature_index = feature_ind
end
end
end
## step 2(c)
#alpha = 1/2 * log((1-err_max)/(err_max))
alpha = 1/2 * log((1.000001-err_max)/(err_max+0.000001))
## step 2(d)
for j = 1:n_sample
pred = 1
x = X[j, feature_index]
if flag * x < flag * threshold
pred = -1
end
w[j] = w[j] * exp(-alpha * y[j] * pred)
end
model.clf[i, :] = [feature_index, threshold, flag, alpha]
end
end
预测模型
function predict(model::Adaboost,
x::Matrix)
n = size(x,1)
res = zeros(n)
for i = 1:n
res[i] = predict(model, x[i,:])
end
return res
end
function predict(model::Adaboost,
x::Vector)
s = 0
for i = 1:model.n_clf
pred = 1
feature_index = trunc(Int64,model.clf[i, 1])
threshold = model.clf[i, 2]
flag = model.clf[i, 3]
alpha = model.clf[i, 4]
x_temp = x[feature_index]
if flag * x_temp < flag * threshold
pred = -1
end
s += alpha * pred
end
return sign(s)
end
接下来应用到模拟例子中
function generate_data(N)
p = 10
x = randn(N, p)
x2 = x.*x
c = 9.341818 #qchisq(0.5, 10)
y = zeros(Int64,N)
for i=1:N
tmp = sum(x2[i,:])
if tmp > c
y[i] = 1
else
y[i] = -1
end
end
return x,y
end
function test_Adaboost()
x_train, y_train = generate_data(2000)
x_test, y_test = generate_data(10000)
m = 1:20:400
res = zeros(size(m, 1))
for i=1:size(m, 1)
model = Adaboost(n_clf=m[i])
train!(model, x_train, y_train)
predictions = predict(model, x_test)
println("The number of week classifiers ", m[i])
res[i] = classification_error(y_test, predictions)
println("classification error: ", res[i])
end
return hcat(m, res)
end
作出误差随迭代次数的图象如下
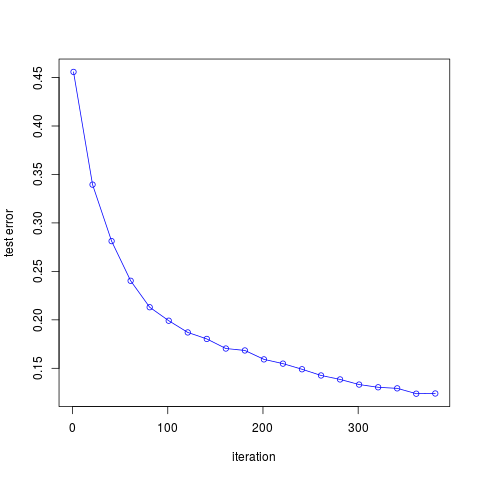
可以发现,随着迭代次数的增加,误差率不断下降,与图10.2的结果是一致的。
完整代码参见这里
R语言实现¶
## generate dataset
genData <- function(N, p = 10)
{
p = 10
x = matrix(rnorm(N*p),nrow = N)
x2 = x^2
y = rowSums(x2)
y = sapply(y, function(x) ifelse(x > qchisq(0.5, 10), 1, -1))
return(list(x = x, y = y))
}
set.seed(123)
train.data = genData(2000)
table(train.data$y)
# y
# -1 1
# 980 1020
AdaBoost <- function(x, y, m = 10)
{
p = ncol(x)
N = nrow(x)
res = matrix(nrow = m, ncol = 4)
## initialize weight
w = rep(1, N)/N
## indicate the classification direction
## consider observation obs which is larger than cutpoint.val
## if flag = 1, then classify obs as 1
## else if flag = -1, classify obs as -1
flag = 1
cutpoint.val = 0
cutpoint.idx = 0
for (i in 1:m)
{
## step 2(a): stump
tol = 1e10
for (j in 1:p)
{
for (k in 1:N)
{
#err = 0
flag.tmp = 1
cutpoint.val.tmp = x[k, j]
# for (kk in 1:N)
# {
# pred = 1
# xx = x[kk, j]
# if (xx < cutpoint.val.tmp)
# pred = -1
# err = err + w[kk] * as.numeric(y[kk] != pred)
# }
xj = x[, j]
pred = sapply(xj, function(x) ifelse(x < cutpoint.val.tmp, -1, 1))
err = sum(w*as.numeric(y != pred))
}
if (err > 0.5)
{
err = 1 - err
flag.tmp = -1
}
if (err < tol)
{
tol = err
cutpoint.val = cutpoint.val.tmp
cutpoint.idx = j
flag = flag.tmp
}
}
## step 2(c)
#alpha = 0.5 * log((1-tol)/tol)
alpha = 0.5 * log((1+1e-6-tol)/(tol+1e-6))
## step 2(d)
for (k in 1:N)
{
pred = 1
xx = x[k, cutpoint.idx]
if (flag * xx < flag * cutpoint.val)
pred = -1
w[k] = w[k] * exp(-alpha*y[k]*pred)
}
res[i, ] = c(cutpoint.idx, cutpoint.val, flag, alpha)
}
colnames(res) = c("idx", "val", "flag", "alpha")
model = list(M = m, G = res)
class(model) = "AdaBoost"
return(model)
}
print.AdaBoost <- function(model)
{
cat(model$M, " weak classifers are as follows: \n\n")
cat(sprintf("%4s%12s%8s%12s\n", colnames(model$G)[1], colnames(model$G)[2], colnames(model$G)[3], colnames(model$G)[4]))
for (i in 1:model$M)
{
cat(sprintf("%4d%12f%8d%12f\n", model$G[i, 1], model$G[i, 2], model$G[i, 3], model$G[i, 4]))
}
}
predict.AdaBoost <- function(model, x)
{
n = nrow(x)
res = integer(n)
for (i in 1:n)
{
s = 0
xx = x[i, ]
for (j in 1:model$M)
{
pred = 1
idx = model$G[j, 1]
val = model$G[j, 2]
flag = model$G[j, 3]
alpha = model$G[j, 4]
cutpoint = xx[idx]
if (flag * cutpoint < flag*val)
pred = -1
s = s + alpha*pred
}
res[i] = sign(s)
}
return(res)
}
testAdaBoost <- function()
{
## train datasets
train.data = genData(2000)
x = train.data$x
y = train.data$y
## test datasets
test.data = genData(10000)
test.x = test.data$x
test.y = test.data$y
m = seq(1, 400, by = 20)
err = numeric(length(m))
for (i in 1:length(m))
{
model = AdaBoost(x, y, m = m[i])
res = table(test.y, predict(model, test.x))
err[i] = (res[1, 2] + res[2, 1])/length(test.y)
cat(sprintf("epoch = %d, err = %f", i, err[i]))
}
return(err)
}
运行速度要比Julia的慢很多。
R GBM实现¶
library(gbm)
## generate dataset
genData <- function(N, p = 10) {
p = 10
x = matrix(rnorm(N * p), nrow = N)
x2 = x^2
y = rowSums(x2)
y = sapply(y, function(x) ifelse(x > qchisq(0.5,
10), 1, -1))
return(data.frame(x, y))
}
set.seed(123)
train.data = genData(2000)
table(train.data$y)
# y
# -1 1
# 980 1020
## train datasets
train.data = genData(2000)
train.data[train.data$y == -1, 11] <- 0
## test datasets
test.data = genData(10000)
test.data[test.data$y == -1, 11] <- 0
# Do training with the maximum number of trees:
Adaboost = TRUE
n_trees = 400
if (Adaboost) {
print("Running Adaboost ...")
m = gbm(y ~ ., data = train.data, distribution = "adaboost",
n.trees = n_trees, shrinkage = 1, verbose = TRUE)
} else {
print("Running Bernoulli Boosting ...")
m = gbm(y ~ ., data = train.data, distribution = "bernoulli",
n.trees = n_trees, verbose = TRUE)
}
training_error = matrix(0, nrow = n_trees, ncol = 1)
for (nti in seq(1, n_trees)) {
Fhat = predict(m, train.data[, 1:10], n.trees = nti)
pcc = mean(((Fhat <= 0) & (train.data[, 11] ==
0)) | ((Fhat > 0) & (train.data[, 11] == 1)))
training_error[nti] = 1 - pcc
}
test_error = matrix(0, nrow = n_trees, ncol = 1)
for (nti in seq(1, n_trees)) {
Fhat = predict(m, test.data[, 1:10], n.trees = nti)
pcc = mean(((Fhat <= 0) & (test.data[, 11] == 0)) |
((Fhat > 0) & (test.data[, 11] == 1)))
test_error[nti] = 1 - pcc
}
plot(seq(1, n_trees), training_error, type = "l", main = "Boosting Probability of Error",
col = "red", xlab = "number of boosting iterations",
ylab = "classification error")
lines(seq(1, n_trees), test_error, type = "l", col = "green")
legend(275, 0.45, c("training error", "testing error"),
col = c("red", "green"), lty = c(1, 1))